
The e-commerce age and accompanying decline of many brick-and-mortar businesses come with changes in customer experience, especially in the retail industry. Brick-and-mortar and brick-and-click (click-and-mortar) businesses can strategically focus on customer experience to counteract the competitive impact of online platforms, like Amazon, eBay, Facebook Marketplace, and Walmart and Walmart Marketplace. The online nature and large scale of these platforms capitalize on cost-effectiveness while reducing or limiting service quality and the associated customer experience. Through customer-focused services designed for excellent customer experience, smaller brick-and-mortar or brick-and-click companies can maintain their competitiveness in the e-commerce age.
Many factors affect brick-and-mortar companies’ competitiveness. However, given the characteristics of the e-commerce age and related market trends, these companies can strategically develop their customer service to remain competitive despite the rise of large online firms like Amazon. The effective application of strategies focusing on customer experience and its related variables can enhance brick-and-mortar competitiveness and long-term success potential.
Customer Experience, Satisfaction and Loyalty
High quality customer experience contributes to customer satisfaction, which in turn builds customer loyalty. Customer service is different from customer experience. While customer service influences customer experience, there are a lot of other variables involved, such as customer preference and mood, social context, and timing, as well as the characteristics of goods, which are not always under the control of the seller in the case of retailing. Even competitors influence how a company’s customer service leads to positive customer experience. Also, in addition to companies’ quality of service, overall economic conditions affect customers’ experience.
Customer experience is about what customers perceive when transacting with providers. For example, customer experience in a small retail store depends on how the customer is accommodated, greeted, and assisted throughout the buying process. In this regard, customer service is a critical success factor that determines customer experience. While it is true that products, such as goods or packaged merchandise, influence customer experience, customer service is the main factor that the provider can control in shaping customer experience. Thus, strategic management initiatives must focus on enhancing customer service as a tool to improve customer experience, for the objective of achieving customer satisfaction and long-term customer loyalty.
Customer loyalty helps ensure the long-term profitability of businesses, especially when competing against large companies with e-commerce operations, like Amazon and Walmart. A company can expect its loyal customers to repeatedly purchase its goods or services. This condition makes business performance more predictable, thereby empowering leaders to implement strategies that are more aligned with the organization and more likely to lead to success. Strategies for high quality customer experience and customer loyalty must encompass human resource development, organizational culture, product quality assurance, and related factors. In building loyalty among customers, a brick-and-mortar business can thrive even in the age of e-commerce that emphasizes efficiency and convenience.
Customer Experience in E-commerce
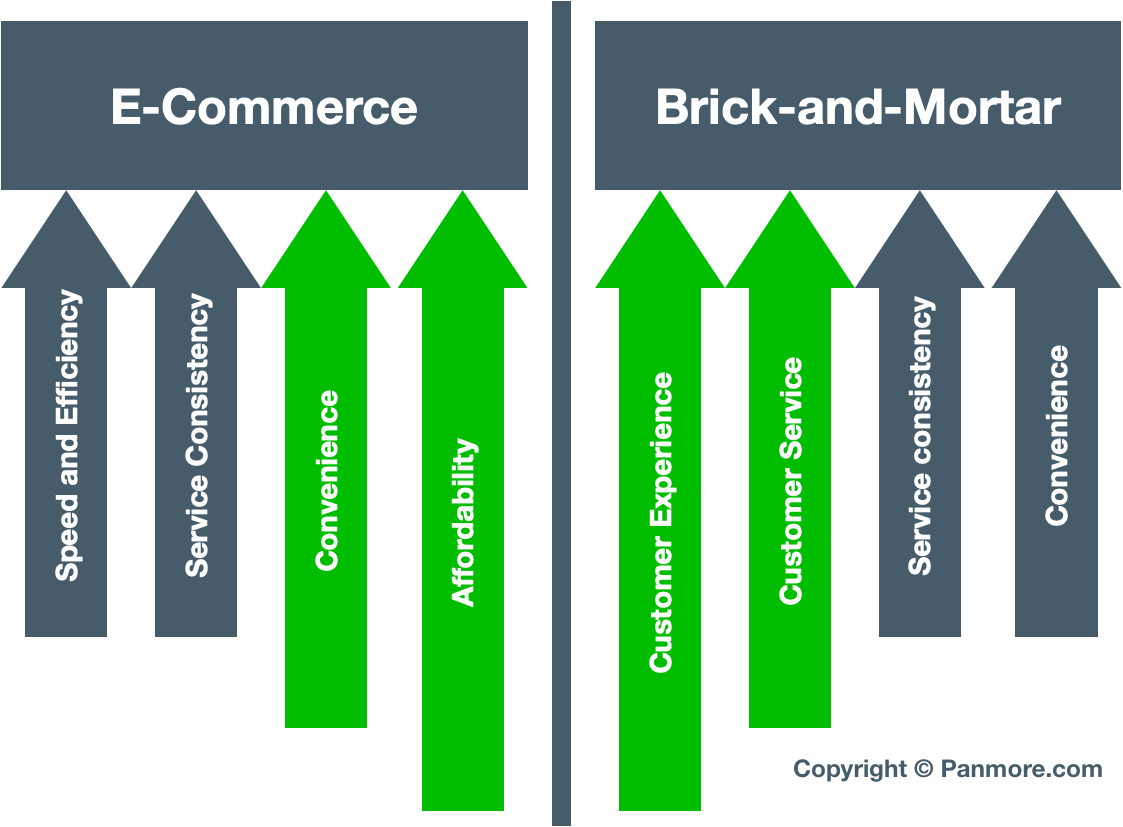
The main competitive advantages of e-commerce companies include efficiency and convenience. In some cases, affordability is also a selling point of online services. For example, customers find it easy to search for and purchase products through Amazon’s website, easily filtering or sorting items based on such variables as product features and price. Customers are attracted to such convenience, in contrast to the time, effort, and money involved in traveling to a retail store to buy goods or pay for services. This condition of ease, convenience, speed, and cost savings of the online environment serves as the primary selling point of e-commerce companies like Amazon, Walmart, and other notable online retailers and service providers.
Considering the focus on efficiency and convenience, many e-commerce businesses neglect to sufficiently support excellence in customer experience. For example, customers are left to make their own assessments of online products, such as based on other customers’ reviews. In addition, it is difficult to achieve high quality customer experience because online companies cannot readily use face-to-face communication and the characteristics of the physical environment to influence customers’ experience and perception of the business. Thus, customer service and, consequently, customer experience, are e-commerce weaknesses that brick-and-mortar and brick-and-click companies can exploit to enhance their competitiveness.
Customer Experience as a Brick-and-Mortar Selling Point
Brick-and-mortar businesses face challenges in maintaining their competitiveness against online companies, especially large ones like Amazon. Nonetheless, customer experience is where brick-and-mortar firms can excel, attract customers, and develop customer loyalty. There are ways of achieving customer loyalty through excellence in customer experience. For example, the brick-and-mortar company can focus on product quality as a way of growing its market share. However, strategic management must put emphasis on how to institutionalize high quality in customer service and excellence in customer experience. This institutionalization helps ingrain the necessary human resource behaviors, knowledge, skills, and abilities for customer experience as a selling point for long-term business competitiveness and success. The following are some of the most strategically significant ways of developing high quality customer experience as a selling point while maintaining a brick-and-mortar or brick-and-click company’s competitiveness in the long term, despite challenges that come with the e-commerce age.
Develop personalized service for customer satisfaction and customer loyalty. Large e-commerce companies typically cannot provide personalized customer service because doing so would cancel out the speed, efficiency, and cost savings linked to using information and communication technologies for large-scale generalized processes for transacting with customers. In contrast, typically smaller brick-and-mortar companies can integrate personalization in their services to improve their competitiveness against e-commerce firms. Personalization can directly differentiate a brick-and-mortar company from large businesses that rely on generalized services. This means that, through personalization, the brick-and-mortar company can attract and retain customers, based on customer experience. High quality personalized customer service contributes to high quality customer experience, which leads to customer loyalty. Implementing personalization requires that the brick-and-mortar business understand the specific needs and preferences of individual customers. Market research is needed to obtain such information and develop strategies accordingly. In small brick-and-mortar businesses, personalization may be easy. For example, the owners of a small local store might personally know customers from the neighborhood, thereby making it easy for the store to provide personalized service to these customers.
Ensure strategic focus on customer service and overall customer experience. In improving customer service and customer experience, companies tend to focus on frontline workers. Understandably, these workers are the ones who have the most significant and direct interaction with customers. However, to effectively improve customer service and overall customer experience, efforts should involve the entire brick-and-mortar business organization. Organizational leaders must include the factors of customer service and customer experience in strategic formulation. For example, top-level strategies must aim for developing the organization’s capabilities in providing and supporting excellent customer experience. These capabilities include training and development programs in human resource management, communication channels for easy communication between customers and the business, databases for efficient access to information that employees need in providing excellent customer service and experience, and other factors that contribute to organization-wide support for high quality customer service. Just as e-commerce firms have organization-wide strategies for IT-based operational efficiency, brick-and-mortar and brick-and-click companies must have organization-wide strategies for excellent customer experience. The organization-wide application of such strategies helps minimize obstacles in excelling in customer experience.
Develop an organizational culture for high quality customer experience. Utilizing an appropriate corporate culture is a strategic approach to providing excellent customer experience. A company’s organizational culture determines how employees behave toward customers. This behavior is a major influence on how customers perceive the business, and their level of satisfaction in transacting with the business. A brick-and-mortar or brick-and-click company can leverage its organizational culture to satisfy customers and achieve excellent customer experience. With a culture aligned with providing excellent customer experience, the brick-and-mortar company can attract customers looking for providers that understand what it takes to satisfy them. A challenge in this strategic approach is that organizational culture is not easily changed, and it takes time to implement changes in a company’s organizational culture. It is best to start a business with an organizational culture that values high quality customer service and experience. In an existing business organization, adjustments in the corporate culture are best achieved through a gradual process that involves all employees, and accounts for workers’ input to the corresponding organizational change.
Support after-sales customer service. A common mistake among businesses, brick-and-mortar and purely online alike, is the narrow focus on service before and during customers’ purchases only. However, after-sales service significantly affects customers’ perception of the business and its products. For example, how a company supports product repair and maintenance after purchase influences customer experience and satisfaction. In this regard, brick-and-click and brick-and-mortar companies can use after-sales service and its corresponding customer experience as a differentiating factor against purely online enterprise that may be unable to provide sufficient or satisfactory after-sales service. Strategic implementation of after-sales service should include the company’s existing sales personnel as part of the team involved in providing after-sales service. This approach streamlines the development of after-sales service because sales personnel can provide the necessary knowledge and experience needed to address customers’ concerns about the products they buy. When properly integrated, after-sales service helps brick-and-mortar firms stand out against businesses that compete based primarily on price, speed, and convenience. An important part of this strategy is that the brick-and-mortar company should include something that purely online/e-commerce companies cannot easily provide, such as a holistically designed experience that makes customers want to come back for more.
Maintain consistency in customer service. Consistency affects customers’ perception and experience. Consistent customer service is attractive because it enables customers to know what to expect from the business. Thus, to develop competitiveness against online giants like Amazon, brick-and-mortar and click-and-mortar companies need to develop consistency throughout their services. Note that Amazon and many other businesses, especially large ones, already have consistent operations and services. In this regard, customer service consistency should be considered a basic and necessary strategic element in developing competitiveness. However, customer service consistency alone does not guarantee the differentiation needed to provide a competitive edge to brick-and-mortar businesses.
Continually develop online operations. Brick-and-mortar businesses should not limit their operations to traditional physical locations and expect long-term success. These businesses need to develop their own online operations, either as support for existing non-online operations, or as a majority component of total operations. The trend to include online presence and e-commerce continues to rise, with international market reach as one of the main benefits. This trend should direct the strategic consideration of brick-and-mortar firms for developing online operations and continually strengthening these operations to complement non-online operations and positively add to customer experience.
References
- Al-Enzi, A., & Al-Enezi, D. (2024). The invasion of e-commerce on SMEs: Exploring the impact on the brick-and-mortar experience. International Journal of Business Information Systems, 46(4), 516-534.
- Fakieh, B., & Wali, A. M. (2024). SMEs and e-commerce. Why or why not? Journal of Infrastructure, Policy and Development, 8(6), 4078.
- Kaur, H. (2024). Digital transformation in retail: Strategies for brick-and-mortar stores. Universal Research Reports, 11(4), 9-16.
- Sharma, N., & Fatima, J. (2024). Influence of perceived value on omnichannel usage: Mediating and moderating roles of the omnichannel shopping habit. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 77, 103627.
- Silva, S. C., Silva, F. P., & Dias, J. C. (2024). Exploring omnichannel strategies: A path to improve customer experiences. International Journal of Retail & Distribution Management, 52(1), 62-88.
- U.S. Department of Commerce – International Trade Administration – Software and Information Technology Industry.
- Zhang, X., Park, Y., Park, J., & Zhang, H. (2024). Demonstrating the influencing factors and outcomes of customer experience in omnichannel retail. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 77, 103622.